Conceptual design
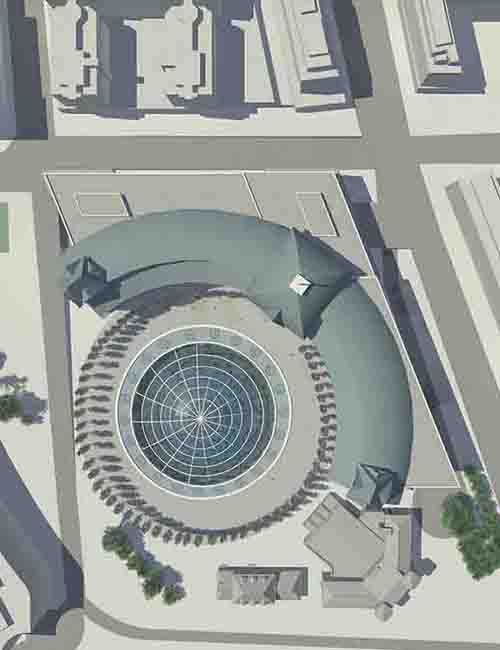

Conceptual design - what is it?
In the fields of design and architecture, “conceptual design” refers to the early stage of the design process where the primary ideas and concepts for a project are developed. This involves:
- Defining the Concept: Formulating the main idea, style, and overall vision for the project, whether it’s a building, interior space, or landscape.
- Creating Sketches and Drafts: Developing initial drawings and visualizations to convey the core ideas and atmosphere of the project.
- Analyzing Requirements and Context: Taking into account client needs, functional requirements, and the characteristics of the surrounding environment and context.
- Developing Alternatives: Proposing and comparing several conceptual solutions to select the most suitable direction.
- Communicating Ideas: Presenting the concept to clients and stakeholders to obtain feedback and approval on the overall direction.
Conceptual design
Conceptual design plays a key role in the successful realization of a project, regardless of its scale and complexity. Here are additional aspects of conceptual design:
1. Creativity and Innovation:
Conceptual design allows for creativity and the implementation of innovative ideas. This is the stage where designers can experiment with new forms, materials, and technologies.
2. Visualization and Presentation:
At this stage, not only sketches and drawings are created, but also 3D models, visualizations, and sometimes even animations. This helps to more clearly present ideas and facilitate their perception by clients and other stakeholders.
3. Functionality and Ergonomics:
Conceptual design takes into account the functional aspects of the project. Designers consider how spaces will be used, how navigation will be organized, and how the project will meet the needs of users.

4. Environmental and Sustainable Solutions:
The conceptual design stage also considers environmental aspects. Designers can incorporate elements of sustainable design into the project, such as the use of eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient solutions, and the integration of natural elements.
5. Social and Cultural Contexts:
Design takes into account social and cultural contexts. This is important for creating spaces that will harmonize with the surrounding environment and cultural characteristics of the locality.
6. Budget and Cost Efficiency:
Although conceptual design primarily focuses on ideas and creativity, it also needs to consider budget constraints. Developing several concepts allows for choosing the most cost-effective solution.
7. Technological Aspects:
Conceptual design includes analyzing the technological feasibility of the project. This helps to determine which technologies and construction methods will be used in the subsequent stages.
8. Feedback and Revision:
Receiving feedback from clients and stakeholders at this stage helps to avoid major changes in the later stages of design and construction. This allows for adapting and refining the concept before its final approval.
9. Documentation:
Conceptual design is accompanied by the creation of documentation, which includes concept descriptions, technical requirements, analyses, and other materials needed to move to detailed design.
Conceptual design is a stage that requires not only creative thinking but also thorough analysis, planning, and communication. It lays the foundation for all subsequent stages of the project, and its quality directly affects the success of the final result.
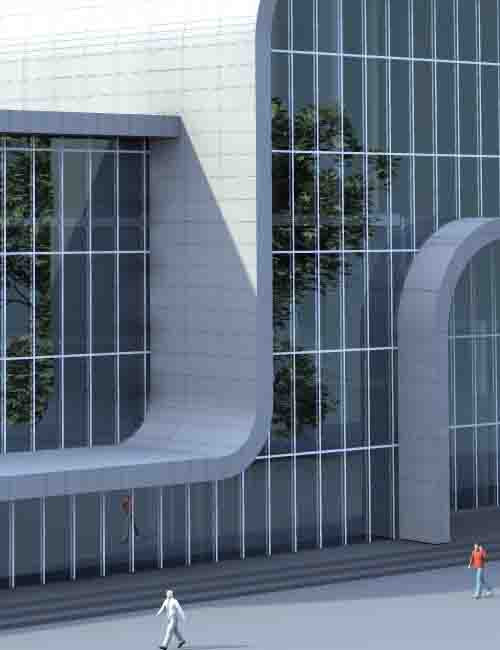
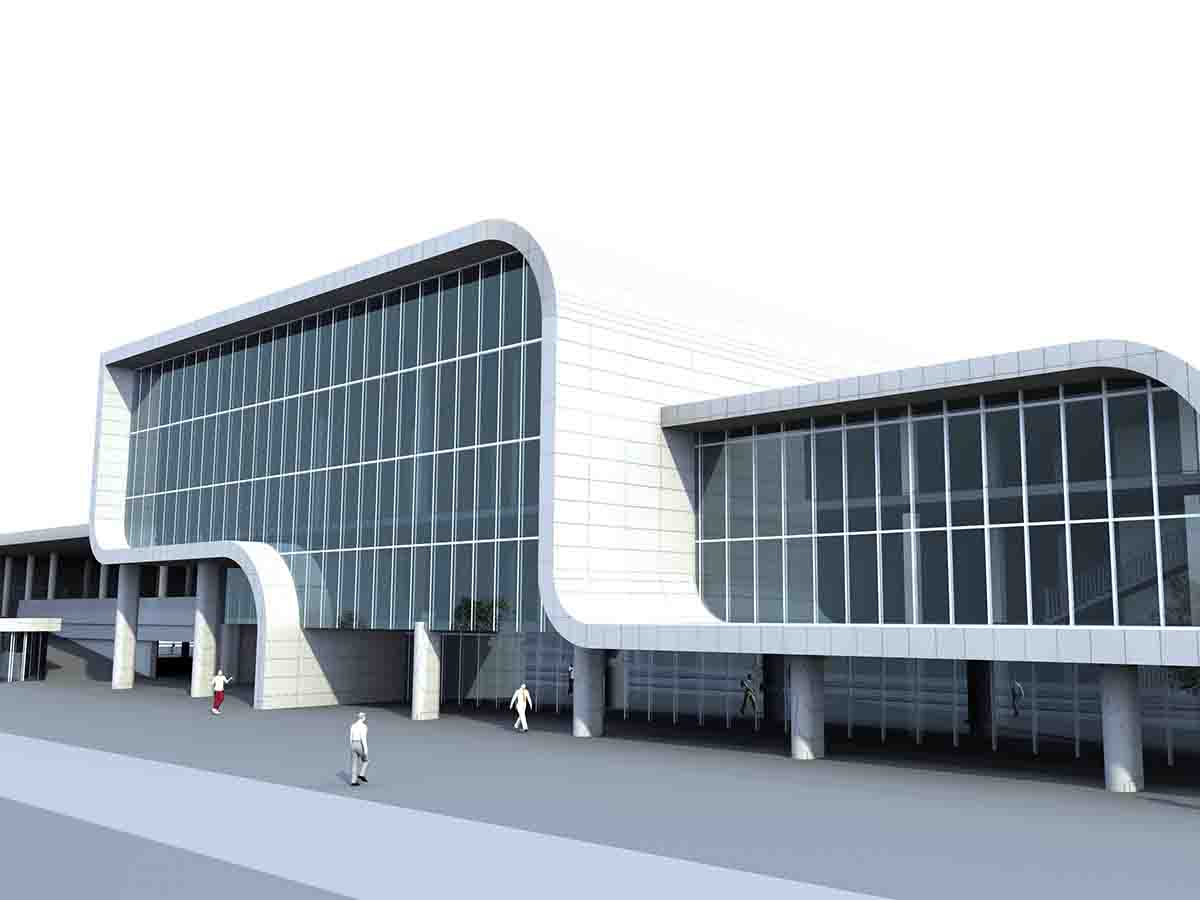
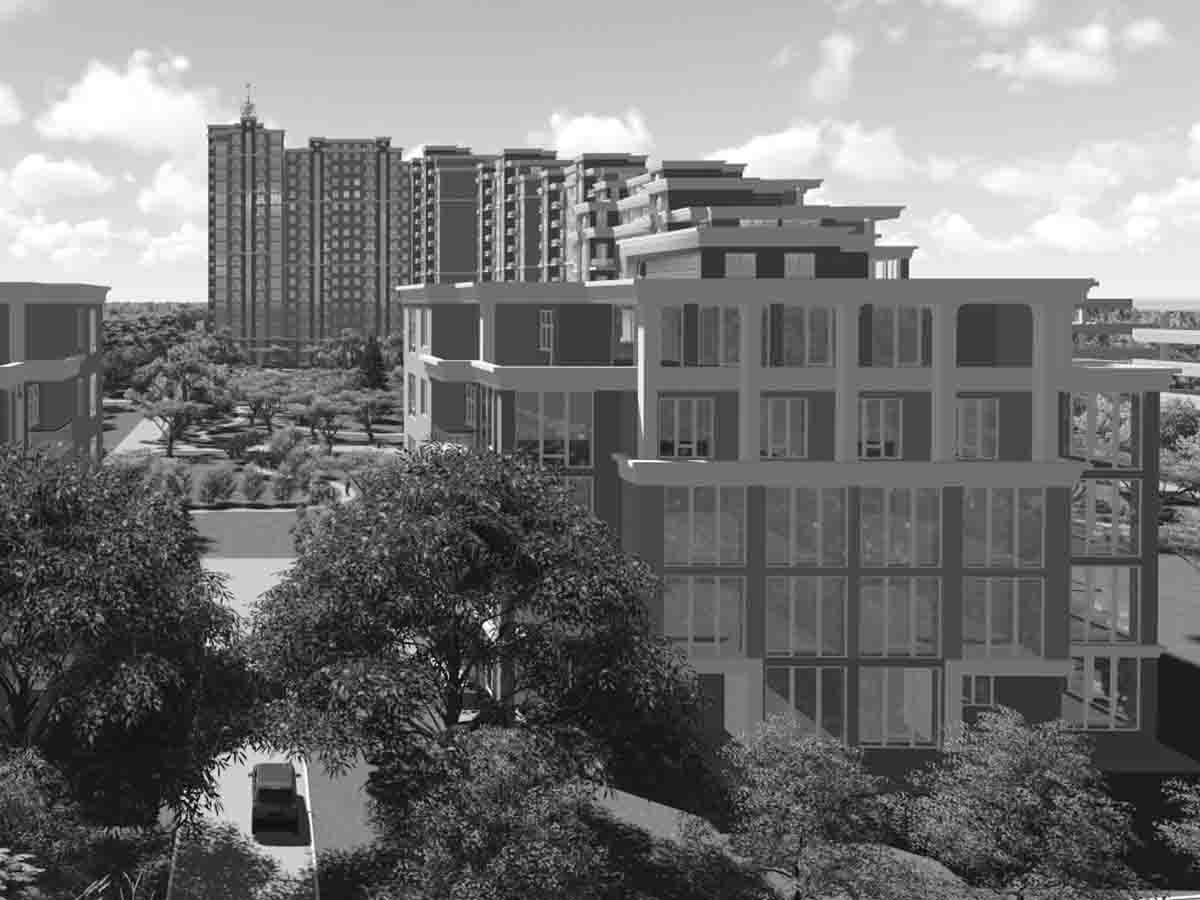
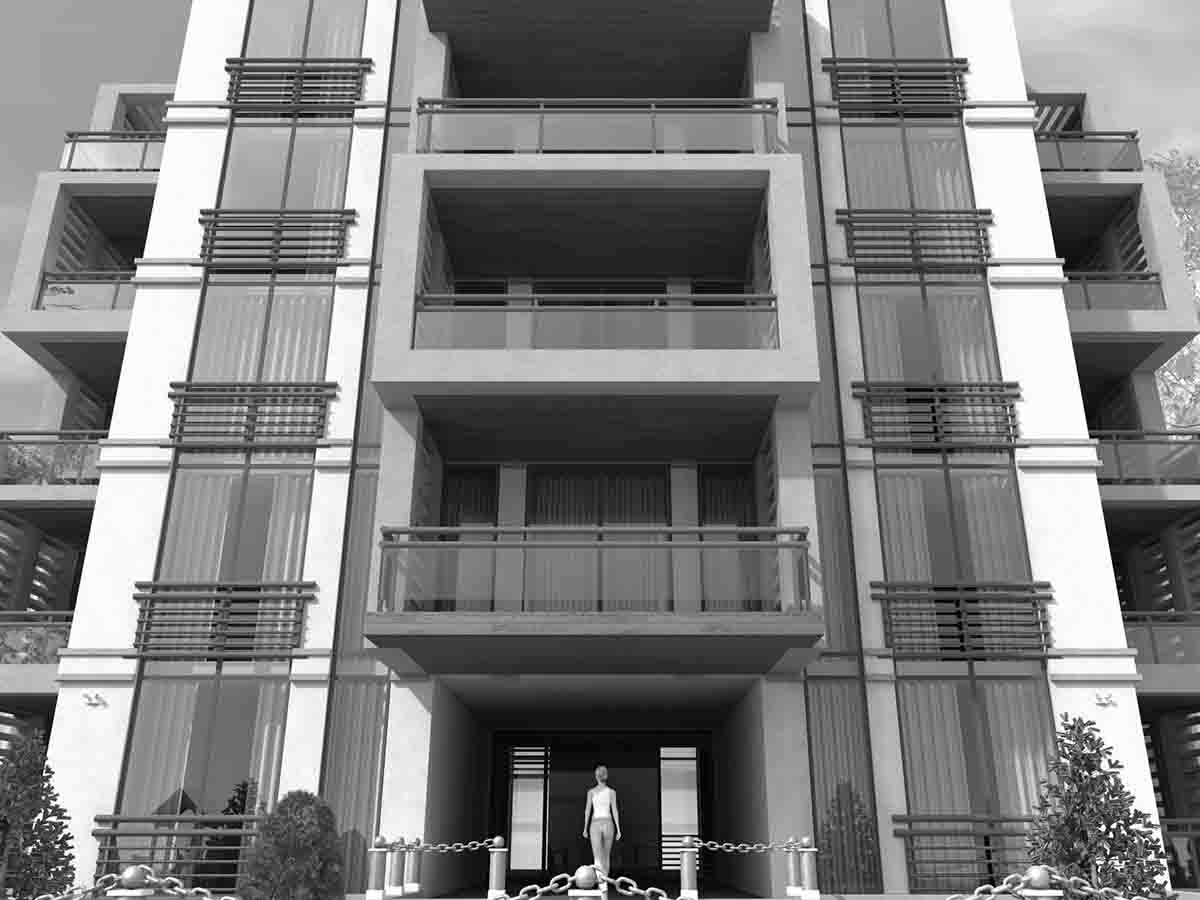
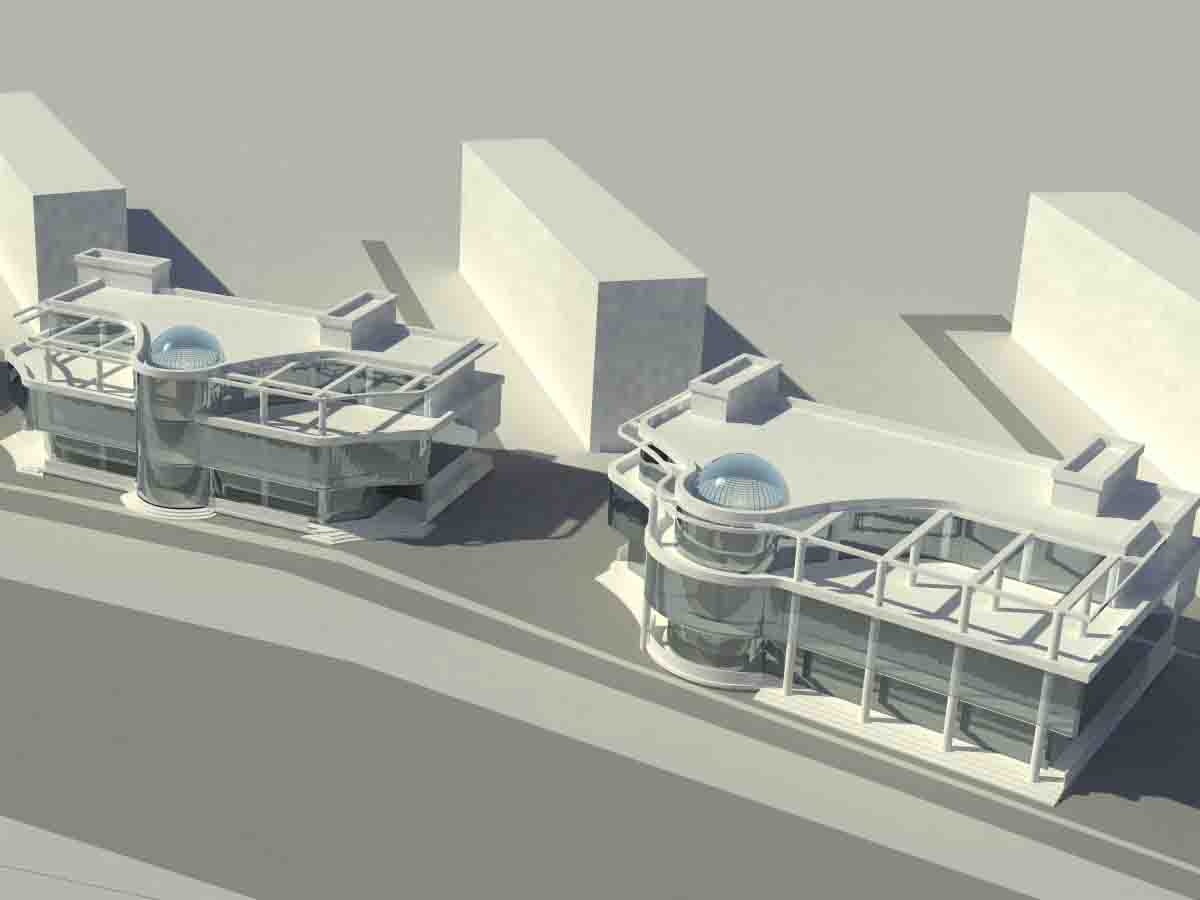
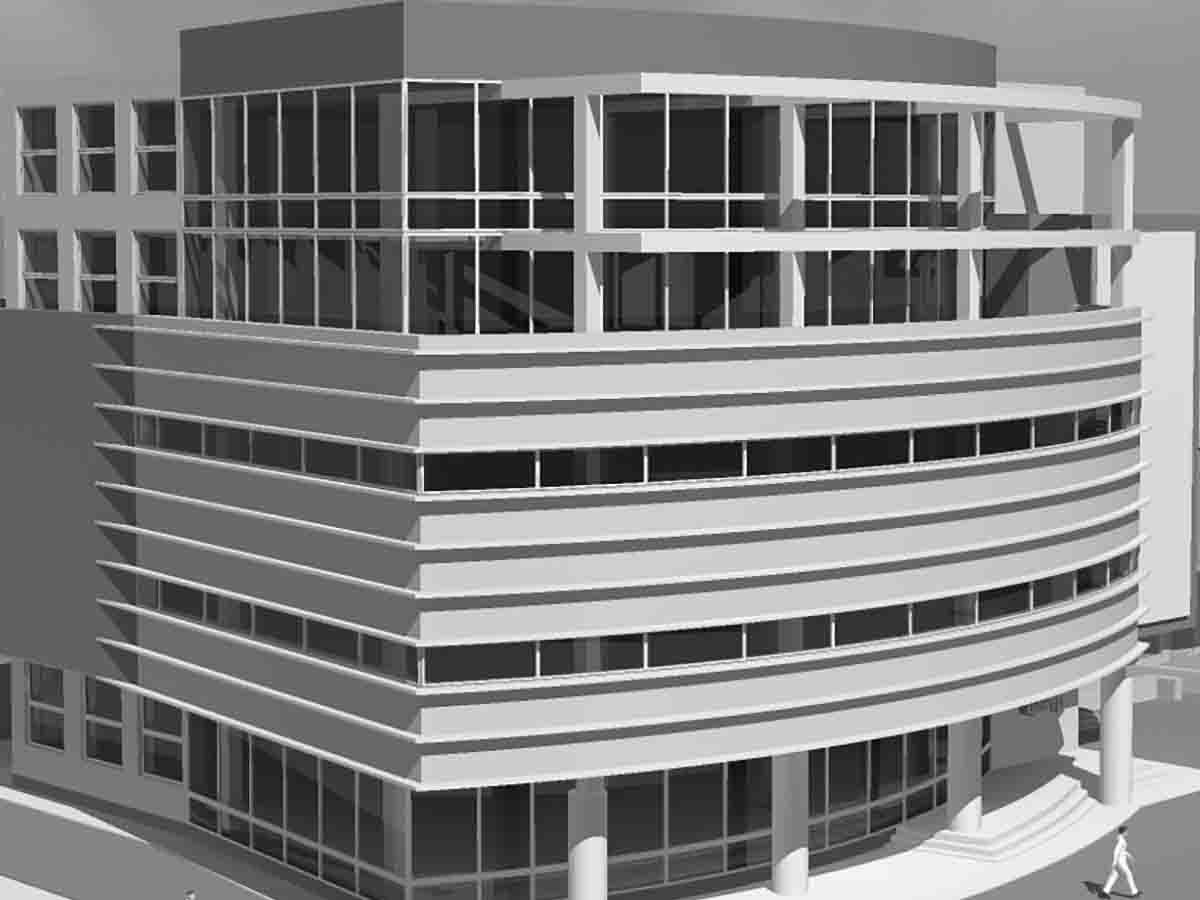
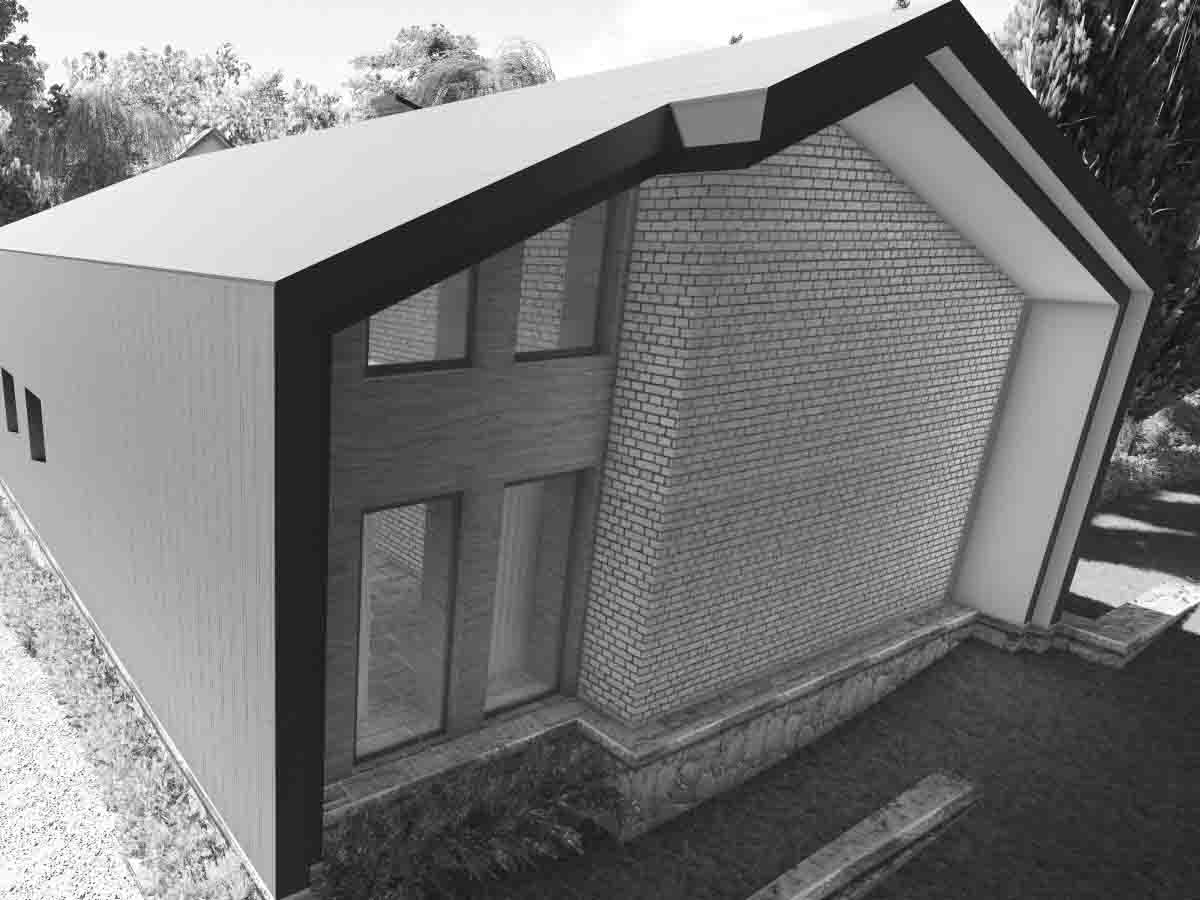
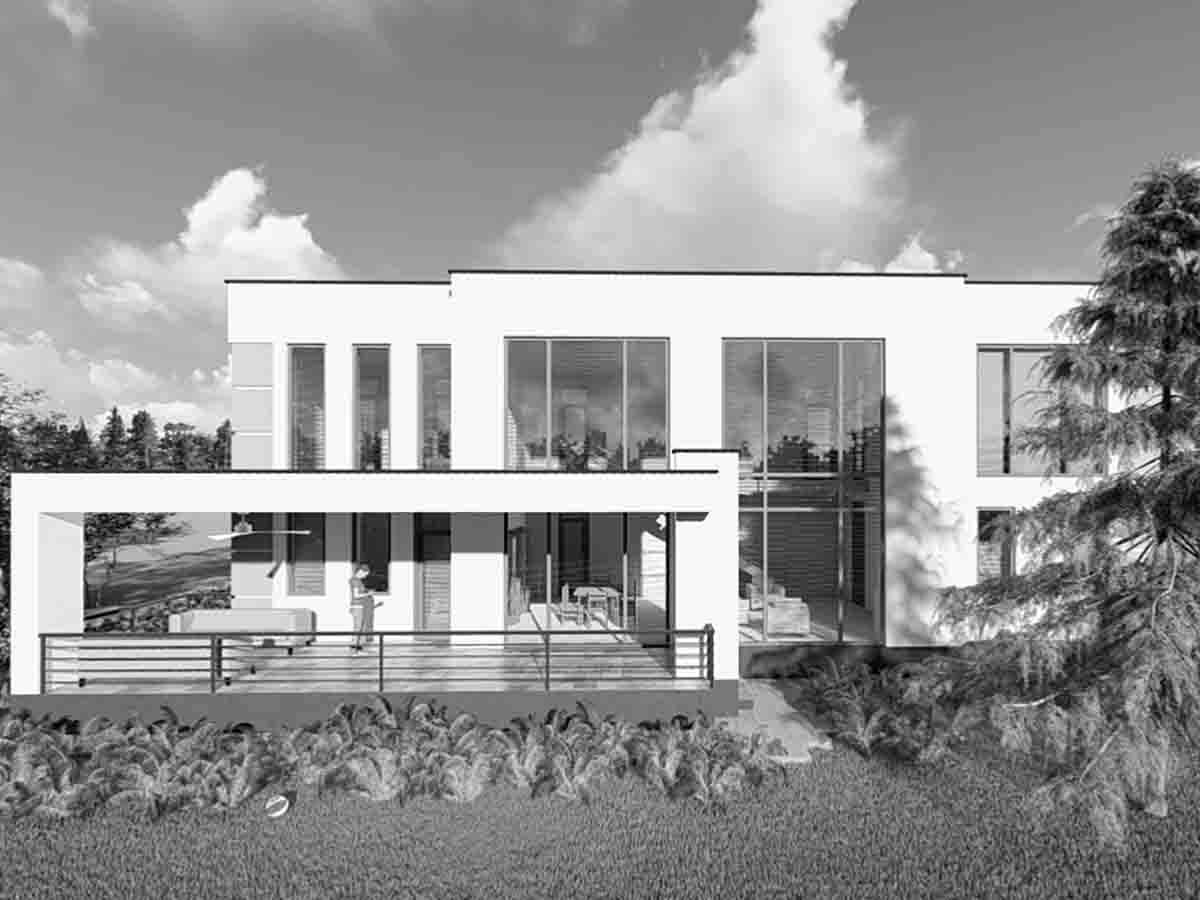
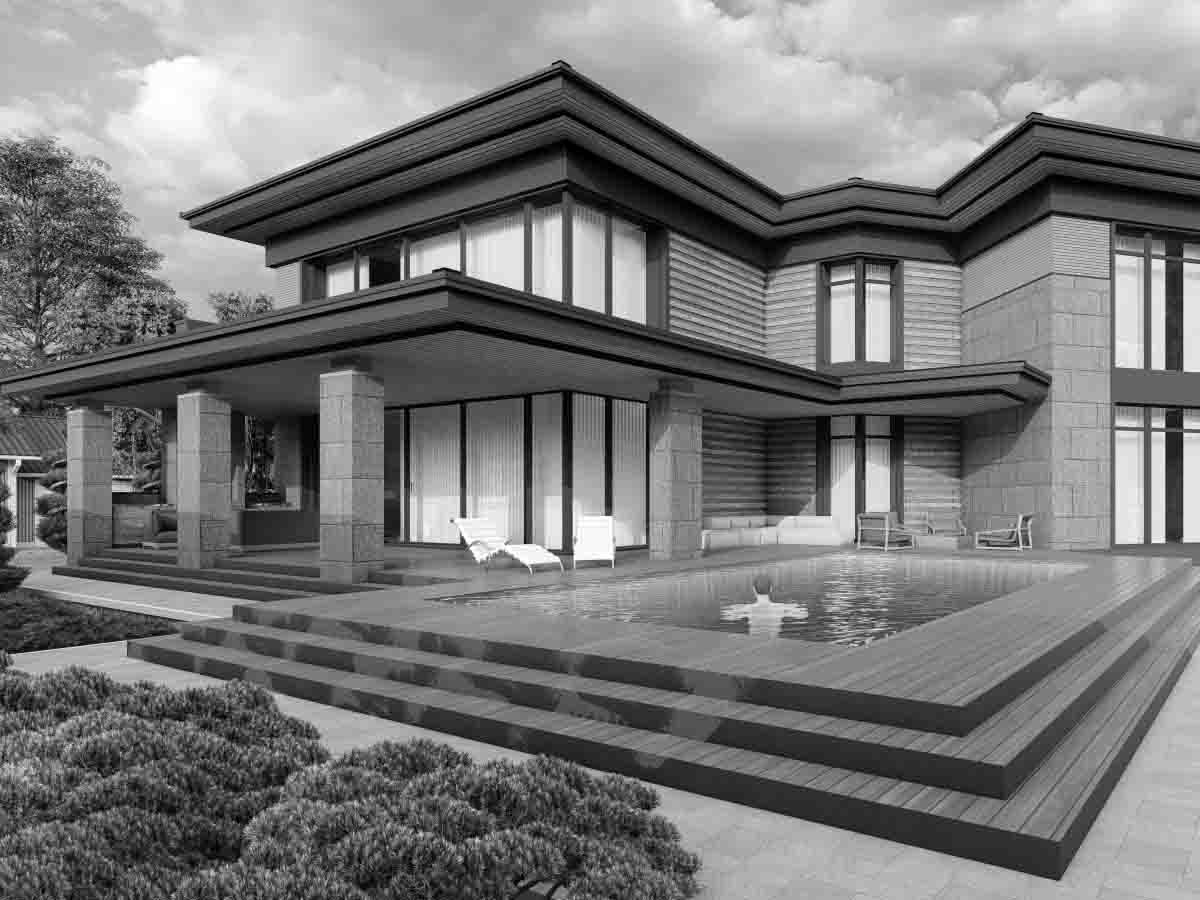









The four main points of conceptual design include
Defining goals and objectives
This involves formulating the main goals of the project and the tasks that need to be accomplished. It includes understanding client requirements, functional needs, and desired outcomes.
Visualizing ideas
Initial sketches, drawings, and 3D models are created to illustrate the core ideas and principles of the future product or system. This helps to visualize the concept and gather feedback from stakeholders.
Generating and evaluating concepts
Various conceptual solutions and ideas are developed to meet the identified requirements. These concepts are evaluated for their viability, functionality, and alignment with the project’s overall goals.
Analyzing and selecting optimal solutions
Different concepts are analyzed considering their advantages and disadvantages, cost, technical feasibility, and other factors. Based on this analysis, the most suitable conceptual solution is selected to be further developed in subsequent stages of design.
These points provide a structured approach to the initial stage of design, laying a solid foundation for the successful implementation of the project.
